|
Carat Color
It may be beneficial to think of the diamond color grades as you might think of the endless variety of shades within a specific color of paint. Imagine you're painting a room and you've settled upon the color beige. You quickly discover that beige is available in a variety of tints and hues. Individually, from one shade or tint to another, the color difference is barely perceptible. It is when only in comparing shades that are several colors apart that the differences become obvious. So it can be with diamond color. Cut
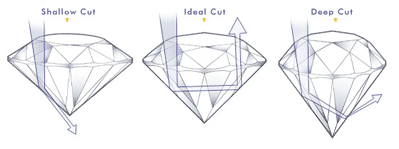
The precision of the cut dictates the amount of light that the diamond will refract and reflect. The more expertly it has been cut, the greater its brilliance will be. When a diamond is cut to Ideal proportions, light is internally reflected from one facet to another and then dispersed through the crown, or top/table of the diamond. If the cut is too deep, then some refracted light will escape through the opposite side of the pavilion, or bottom of the diamond. If the cut is too shallow, then some light will escape through the pavilion before it can be reflected. A well-cut diamond is comprised of facets with the correct angles perfectly placed to maximize the diamond's brilliance. It is the quality of the cut and final polish that reveals the beauty of a diamond.
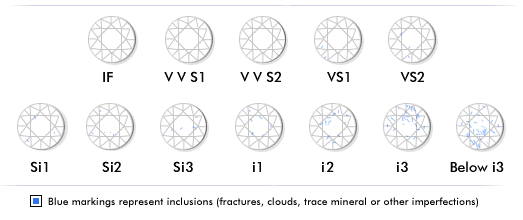
Clarity A diamond is carbon that crystallizes in the earth for millions of years. During the crystallization process a variety of inclusions in the crystalline structure may occur. These inclusions, described by terms such as: cloud, feather, dark inclusions, etc., are found in almost every diamond and are generally caused by conditions present when the diamond was formed, though blemishes may also occur during the polishing process. The grading for clarity measures how many or few of these flaws are found, and gives special consideration to where they are located in the diamond.
Since nature makes nothing absolutely pure or perfect, those diamonds with few inclusions are most rare and command a higher price. The industry wide scale ranges from the low end or imperfect I-3, to the best "gem quality", the internally flawless IF/FL. Certification Reputable diamond certification laboratories include Gemological Institute of America (GIA), The European Gemological Laboratory (EGL), The American Gem Society (AGS), The International Gemological Institute (IGI), and Hoge Road voor Diamant or Diamond High Council (HRD). These grading laboratories all utilize the same methodology of diamond grading including evaluating a specific diamond's 4c's by three separate gemologist. The final grade is determined by a majority opinion as to cut, color, clarity and carat weight. There are other laboratories that exist that offer diamond grading certificates. They vary in reputation and accuracy and you should be advised to evaluate their credentials before choosing to entrust your diamond with them. |